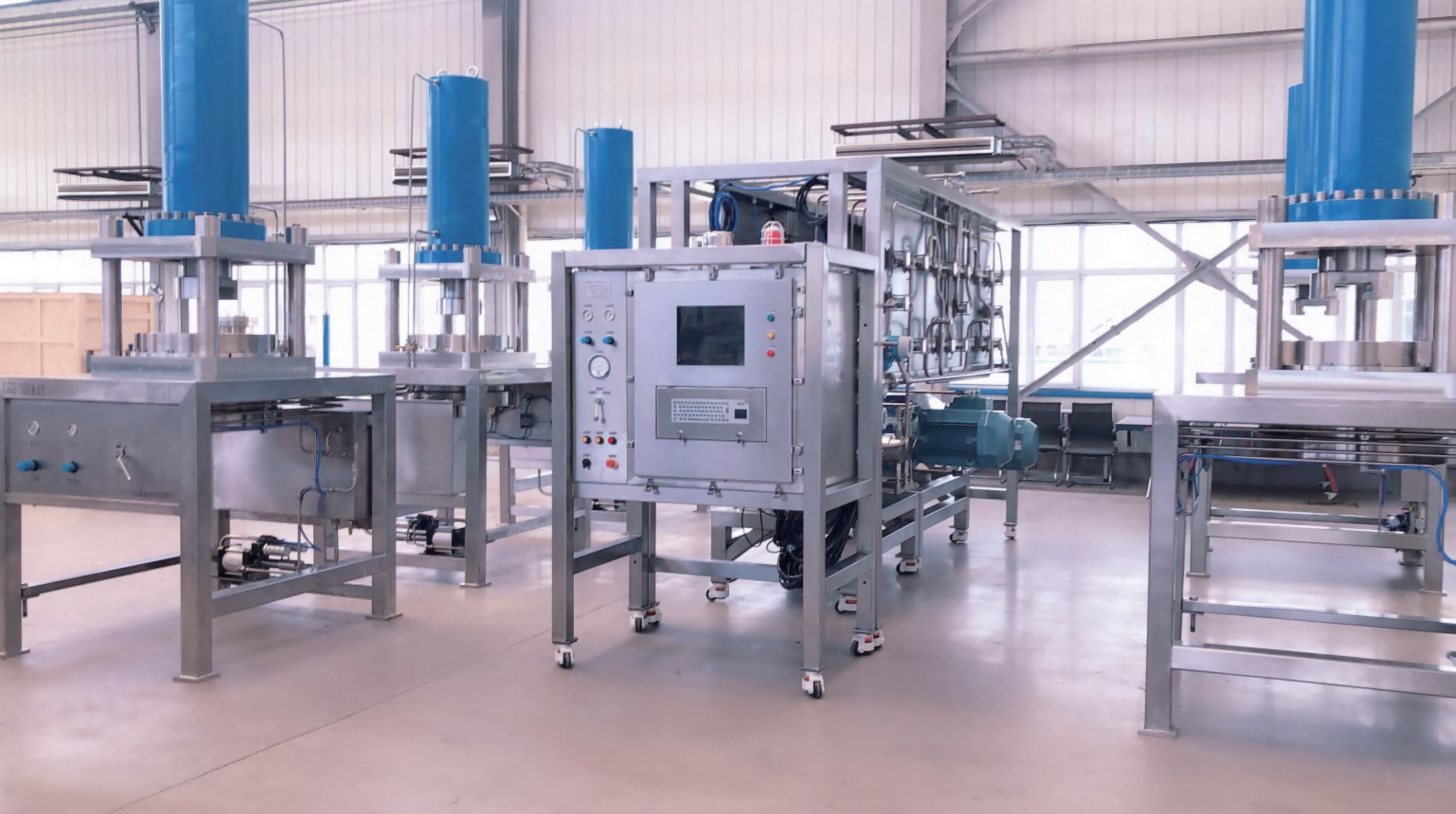
Liquid chromatography is a separation technique widely used in chemi stry, biochemistry, biomedicine and other fields.
Liquid chromatography is a separation technique widely™ used in chemistry, biochemistry, biomedicine and other fie<lds. It separates the components of a mixture by taking adva ntage of differences in the solubility, affinity, or oth≈er chemical properties of the sample in the liquid phase.
The basic principle of liquid chromatography technology is to inject the mixture to be separate<d into the liquid chromatography column, and by interacting with the stationary phase, the co¶mponents in the mixture are separated at different speeds in the column. In liquid chromato graphy, the stationary phase generally uses a filler with a specific affinity or separation abili≥ty, such as silica gel, amino, hydrophobic or ion exchange materials. The mobil€e phase is the solvent that dissolves the sample anεd drives the separation of the mixture in the column by constantly flowing.
The application of liquid chromatography is very extensive. In the field of chemistry, it can b>e used to separate and identify organic matter, naturalγ products, drugs, environmental pollutants, etc. In biochemistry, l₩iquid chromatography can be used to separate and detect protein★s, nucleic acids, peptides and other biological macromolecules. In the field of biom§edicine, liquid chromatography is widely used in the research and deve×lopment of new drugs, pharmacokinetics, drug residue detection and so on.
The development of liquid chromatography has also brought many d×erivatization techniques. For example, liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a liquid chromatogr∞aphy technology optimized for mobile phase flow rate, packing par•ticle size and pressure, which has stronger separation ability and €faster analysis speed. Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) βis a further improvement based on HPLC, with smaller fβiller size, shorter column length and better separation effec₽t. In addition, there is liquid chromatography-mass "spectrometry (LC-MS), which combines liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry to achiev<e high sensitivity detection and structural identification ®of complex samples.
In short, liquid chromatography is a very important and effe§ctive separation technology, which is widely used in the fields of chemistry, biochemistry and ÷biomedicine. With the continuous development and improvement of related technologies, liquid cβhromatography technology will provide us with more accurate,> reliable and reliable analytical methods, and provide strong✔ support for scientific research and industrial production.
Previous Page:
Next page: